50+ Generative AI Statistics 2024

Generative AI has grown exponentially since the groundbreaking release of ChatGPT in November 2022. With millions using the chatbot and other similar tools to complete tasks in ways that would’ve been unthinkable even a year earlier, 2023 became dubbed by many as ‘the year of generative AI’.
The boom has continued in 2024, with the technology’s popularity soaring as its functionality improves.
But what does the future of generative AI look like? To find out more, AIPRM has compiled over 100 generative AI statistics to look at areas such as market size, usage stats, and public opinions on generative AI.
Top 10 generative AI statistics 2024 #
- The global generative AI market was valued at nearly $45 billion in 2023, and is expected to be worth more than $200 billion by 2030 (+361%).
- The generative AI industry generated nearly $68 billion in revenue in 2023 – up more than two-thirds (68%) from 2022.
- Around two-fifths (41%) of the global generative AI market is based in North America – the most of any region.
- More than two-thirds (68%) of generative AI users had used the software to ask a question – the highest number of any task.
- Nearly two-thirds (64%) of business leaders feel a high urgency to adapt to generative AI.
- Over a third (34.7%) of millennials used generative AI at least once a month in 2023.
- Almost three-fifths (59%) of men said they used generative AI in 2024, compared to just over half (51%) of women.
- Less than two-fifths (37%) of marketers used generative AI to assist with daily work tasks in 2023 – the most of any industry.
- More than two-fifths (44%) of businesses surveyed in 2023 expect generative AI to reduce their workforce in the following three years.
Generative AI market statistics #
The latest generative AI statistics found the global value of the generative AI market stood at nearly $45 billion in 2023. This represents a nearly sevenfold increase from 2020 (+692%) and means the industry almost doubled in value (+94%) between 2022 and 2023.
A breakdown of the total value of the global generative AI market from 2020-2023 and the projected value from 2024-2030 #
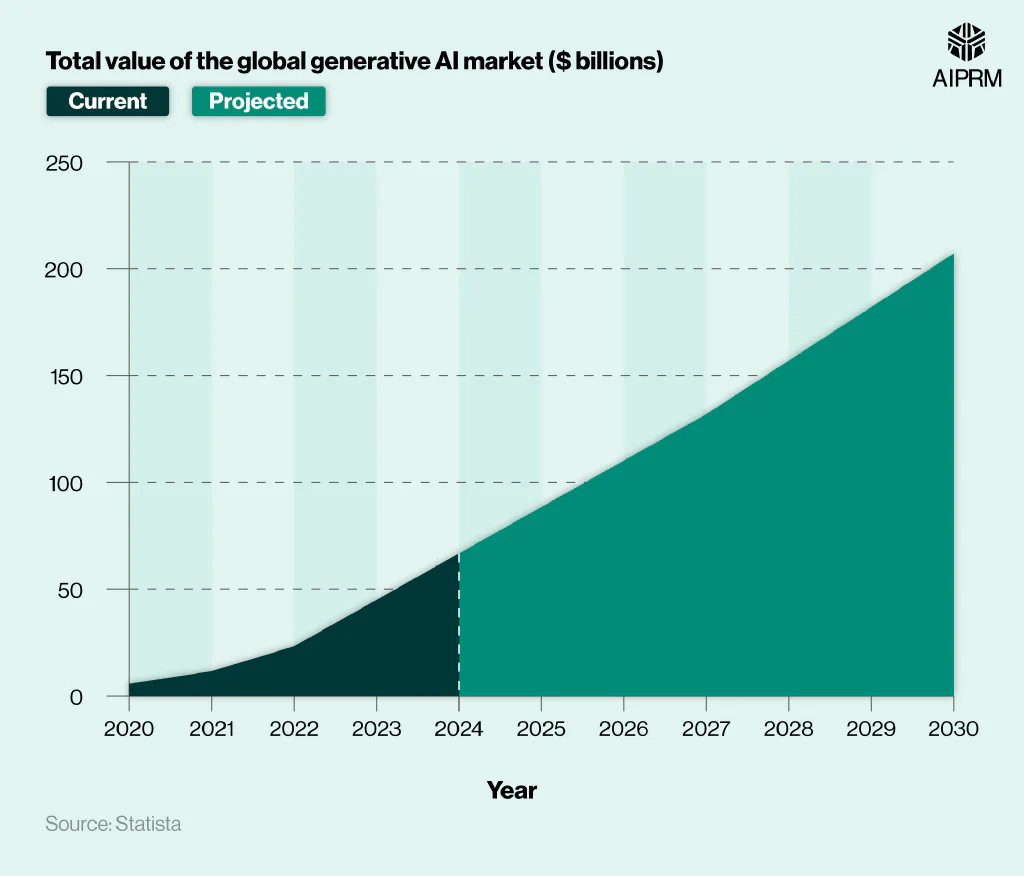
The generative AI industry almost doubled in value every year between 2020 and 2023, with growth expected to slow slightly from 2024 onwards.
Global industry value is expected to surpass $66 billion in 2024, representing a rise of just under half (+49%) from the previous year. Much of this growth will come from the US market, with the value of the US generative AI industry expected to surpass $23 billion by the end of 2024. If correct, then the US earnings would account for more than a third (35%) of the projected global revenue.
From here, the global market is expected to grow further, rising past $88 billion in 2025 (+33%) before exceeding $110 billion in 2026 (+25%). The following few years are predicted to see annual rises of at least $20 billion, with total market value reaching nearly $207 billion by 2030.
If these figures are correct, it would mean that the global generative AI industry would more than quadruple in value (+361%) between 2023 and 2030.
How much revenue does generative AI generate? #
Analysis of generative AI statistics found that the industry generated $67 billion in revenue in 2023 – a rise of over two-thirds (68%) from the previous year. This means that generative AI is now responsible for a fiftieth (2%) of all global I.T. revenue, having more than quadrupled in value (+378%) since 2020.
A breakdown of global generative AI industry revenue between 2020 and 2023 and the projected revenue from 2024-2032 #
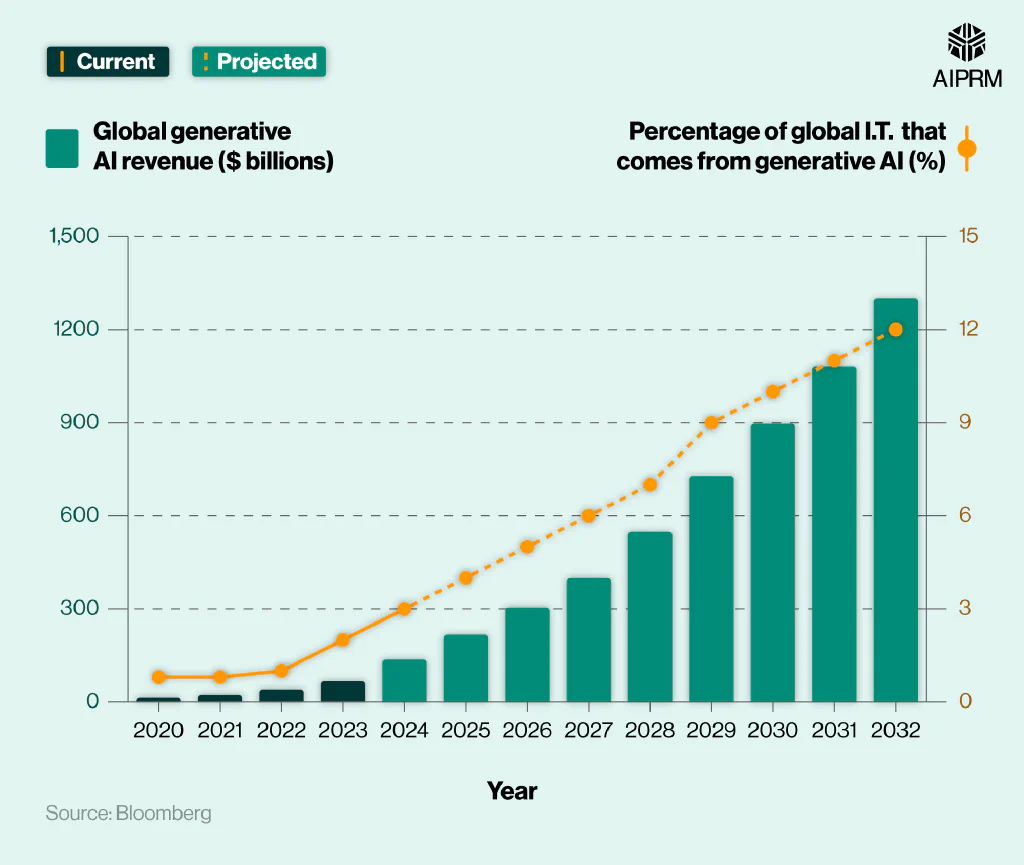
Industry revenue is expected to double (104%) between 2023 and 2024, surpassing $100 billion for the first time. An annual rise of more than half (+58%) will see earnings reach $217 billion in 2025, before surpassing $300 billion a year later (+40%).
Between 2026 and 2030, global generative AI revenue is expected to almost triple (+195%), reaching $897 billion. A fifth increase (20%) between 2030 and 2031 is predicted to take industry earnings past $1 trillion, with a similar rise taking revenue to $1.3 trillion a year later.
If predictions are correct, it will mean that the generative AI market will create nearly 20 times (+1,840%) more revenue in 2032 than it did in 2023. The industry is also expected to account for over a tenth (12%) of all I.T. revenue by this time – a rise of 11% from 2023.
What are the main areas fueling generative AI growth? #
Generative AI software is projected to create more than a quarter of a billion ($280 billion) in revenue by 2032. This would account for more than a fifth (21%) of total projected industry revenue and mean that generative AI software experiences a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 69% between 2022 and 2032.
Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) is expected to be the next highest income stream, generating $247 billion. This would account for just under a fifth (18%) of projected industry revenue and represent a CAGR of 60% over the previous decade.
A breakdown of the AI sectors projected to generate the most revenue in 2032 #
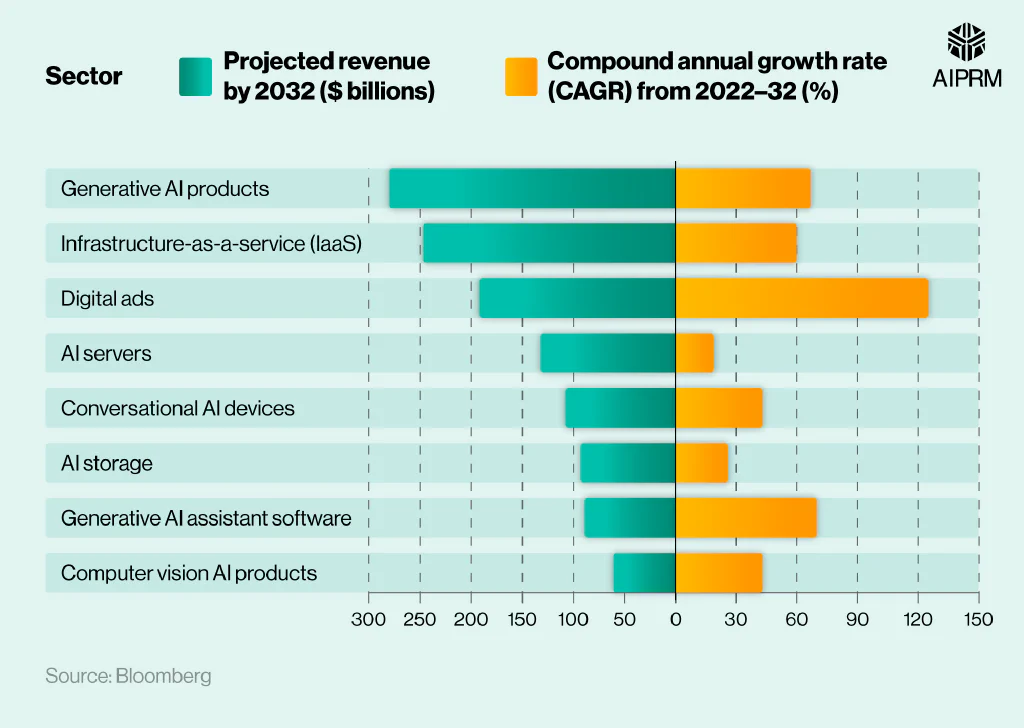
AI-powered digital ads are predicted to generate more than $190 billion by 2032 – a CAGR of 125% and equivalent to 15% of projected industry revenue. This means that the combined earnings of the top three income sources are expected to be worth more than half (54%) of the overall revenue of the generative AI industry by 2032.
Rounding off the top five are AI servers and conversational AI devices, with projected earnings of $132 billion and $108 billion, respectively. Combined, this would equate to just over 18% of the projected generative AI industry revenue of $1.3 trillion.
Which region has the largest generative AI market share? #
Recent generative AI stats show North America held the highest portion of the global generative AI market in 2022. With more than two-fifths (41%) of the entire market situated in North America, the region had a 15% higher market share than any other area.
A breakdown of the regions with the highest percentage of the global generative AI market share (2022) #
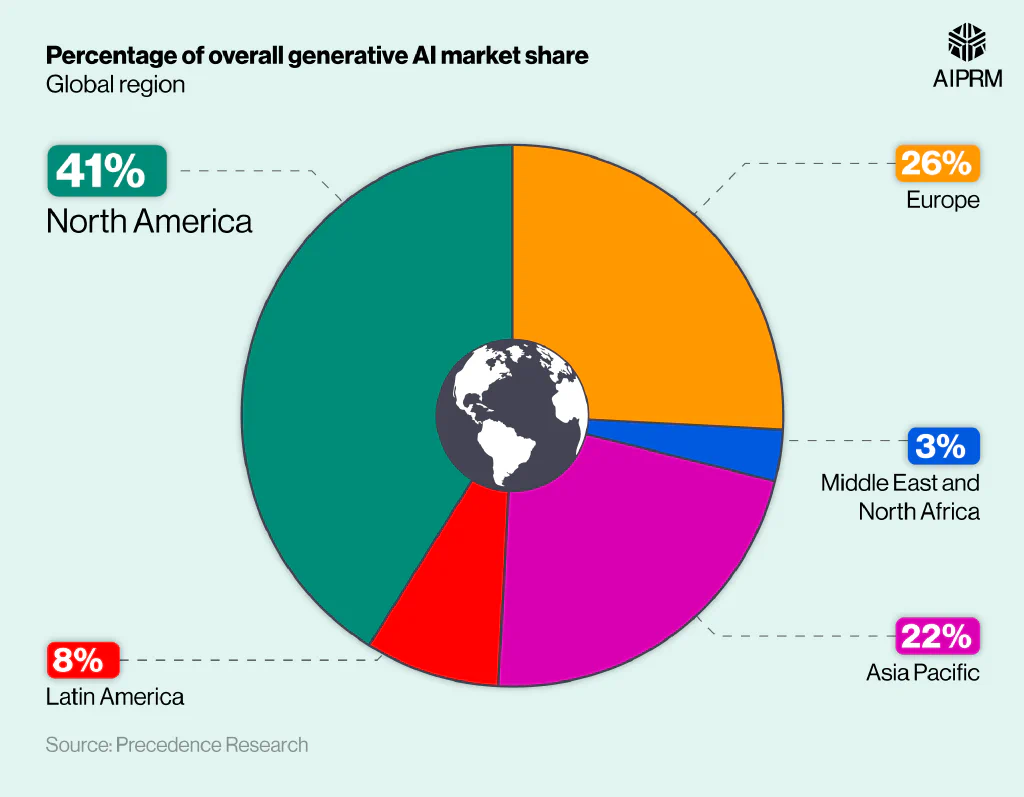
Europe had the next highest percentage, with more than a quarter (26%) of the generative AI industry based there. This was 4% more than the next highest region (Asia Pacific), meaning North America and Europe’s combined market share accounts for more than two-thirds (67%) of the global industry.
The Middle East and North Africa were responsible for just 3% of the global generative AI market in 2022, combined. This was less than half the total of Latin America (8%) – the region with the next lowest market share.
Investment in generative AI #
Analysis of generative AI statistics found that global generative AI investment increased fourfold (+407%) between 2022 and 2023. After a decline in 2022, which saw total investment fall to $4.3 billion (-47%), funding soared in 2023, reaching $21.8 billion.
A breakdown of the total investment in the global generative AI industry between 2019 and 2023 #
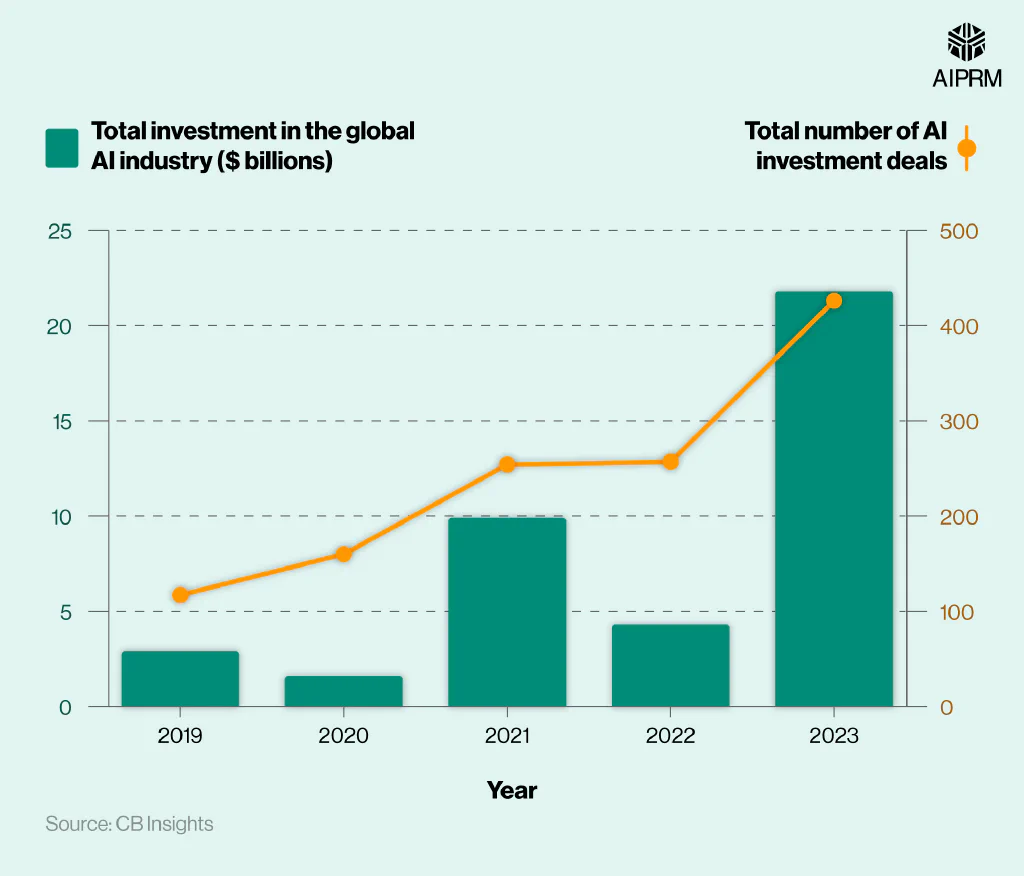
Investment in generative AI fluctuated between 2019 and 2023. After total investment of $2.9 billion in 2019, numbers nearly halved (-44%) in 2020 to $0.6 billion. This was followed by a five-fold increase (+519%) in 2021 before almost halving again a year later.
The latest figure means global generative AI investment was more than seven times greater (+652%) in 2023 compared to 2019.
At the same time, the total number of investment deals has increased year-on-year. After 117 deals were recorded in 2019, numbers rose by more than a third (37%) in 2020 and nearly three-fifths (+60%) a year later.
After a marginal increase in 2022 (+1.2%), the total number of deals rose two-thirds (+66%) a year later, reaching 426 – more than triple (+264%) the number from 2019.
Which generative AI companies are getting the most investment? #
Open AI was the generative AI business that received the most funding in 2023. The company behind ChatGPT received a total investment of $10 billion – five times more than any other company.
This means that investment in Open AI accounted for nearly half (46%) of total industry funding in 2023.
A breakdown of the generative AI companies that received the most investment in 2023 #
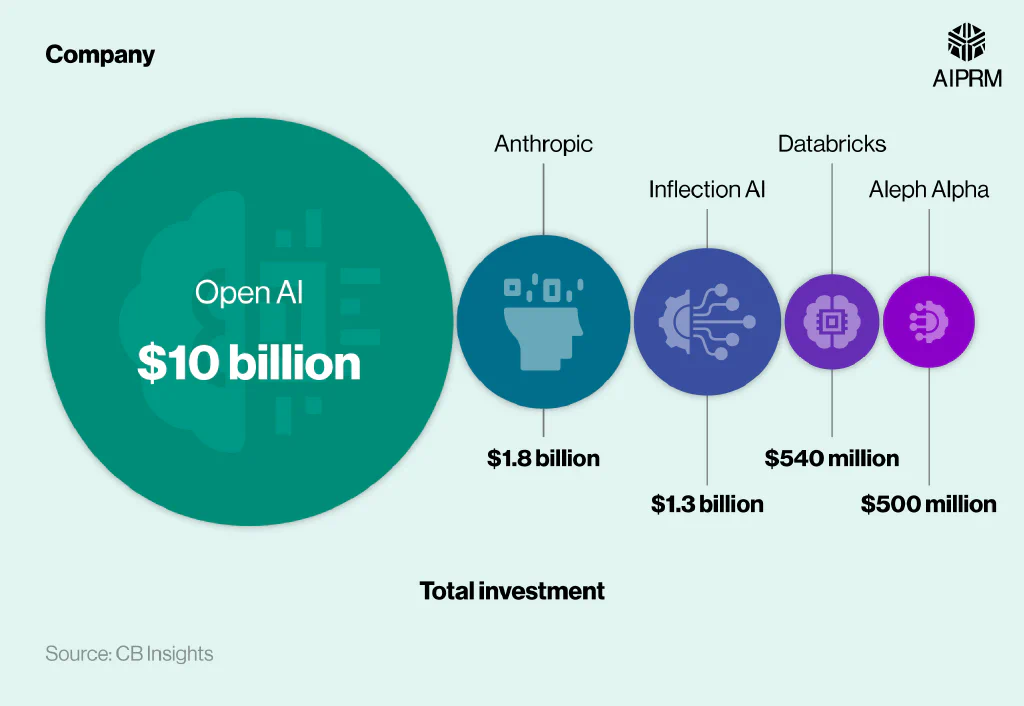
California-based companies Anthroptic ($1.8 billion) and Inflection AI ($1.3 billion) received the second and third-highest investment totals, respectively. These were the only other companies to receive more than $1 billion of investment in 2023, with their combined funding accounting for 14% of the industry total.
German AI startup Aleph Alpha was the only non-American company in the top five, with a total investment of $500 million, according to Generative-AI statistics. This was a twentieth (5%) of the Open AI total and the fifth-highest overall.
Generative AI usage statistics #
A 2023 report from Statista looked at the responses of 2,000 generative AI users to identify the most common reasons people were using the technology.
More than two-thirds (68%) of respondents used generative AI to answer a question – 14% more than any other task. Brainstorming was the next most common task, with a score of 54% making it the only other task performed by more than half of generative AI users.
A breakdown of the most common ways generative US AI users utilize the software #
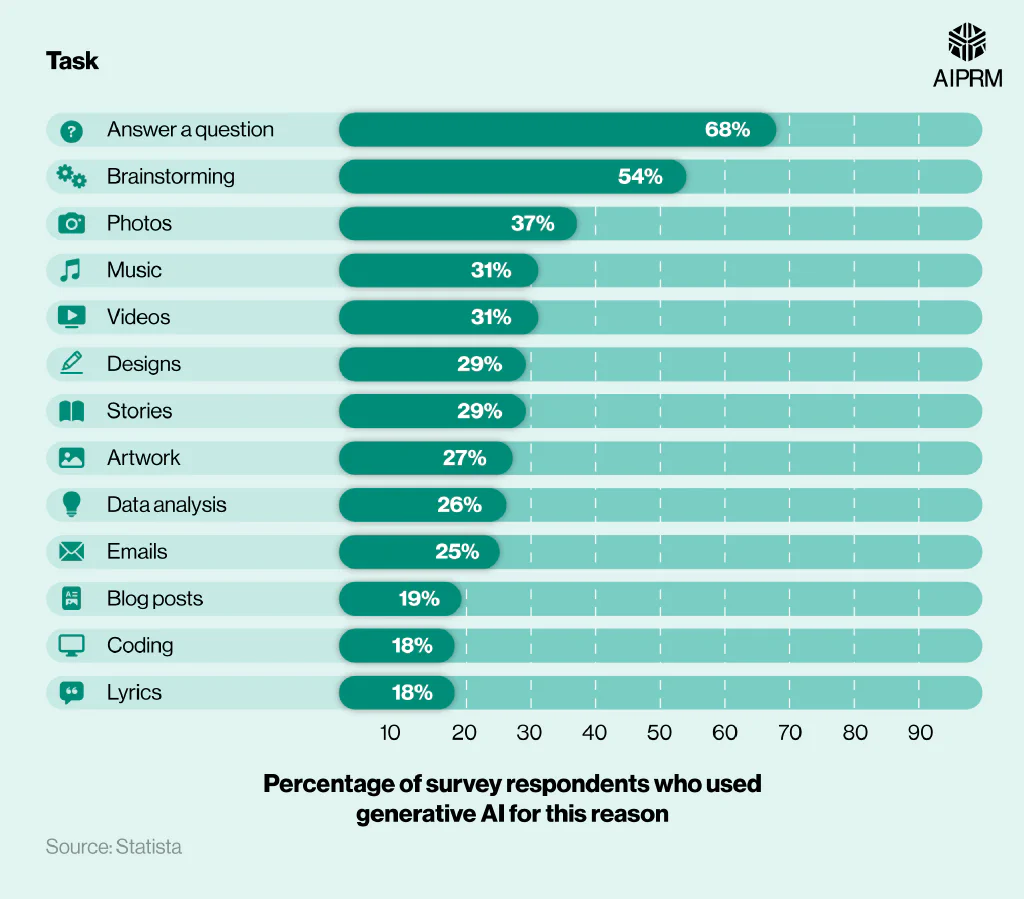
Over a third (37%) of respondents used generative AI for assistance with photos – 17% less than those who used it to brainstorm. Around three-tenths (31%) used it to create music or video, making them the only other tasks performed by more than 30% of users.
At the other end of the scale, less than a fifth of respondents utilized generative AI to write blog posts (19), write lyrics (18%), or code (18%). These were the only tasks included in the study performed by less than a quarter of respondents.
A breakdown of the most commonly used types of generative AI #
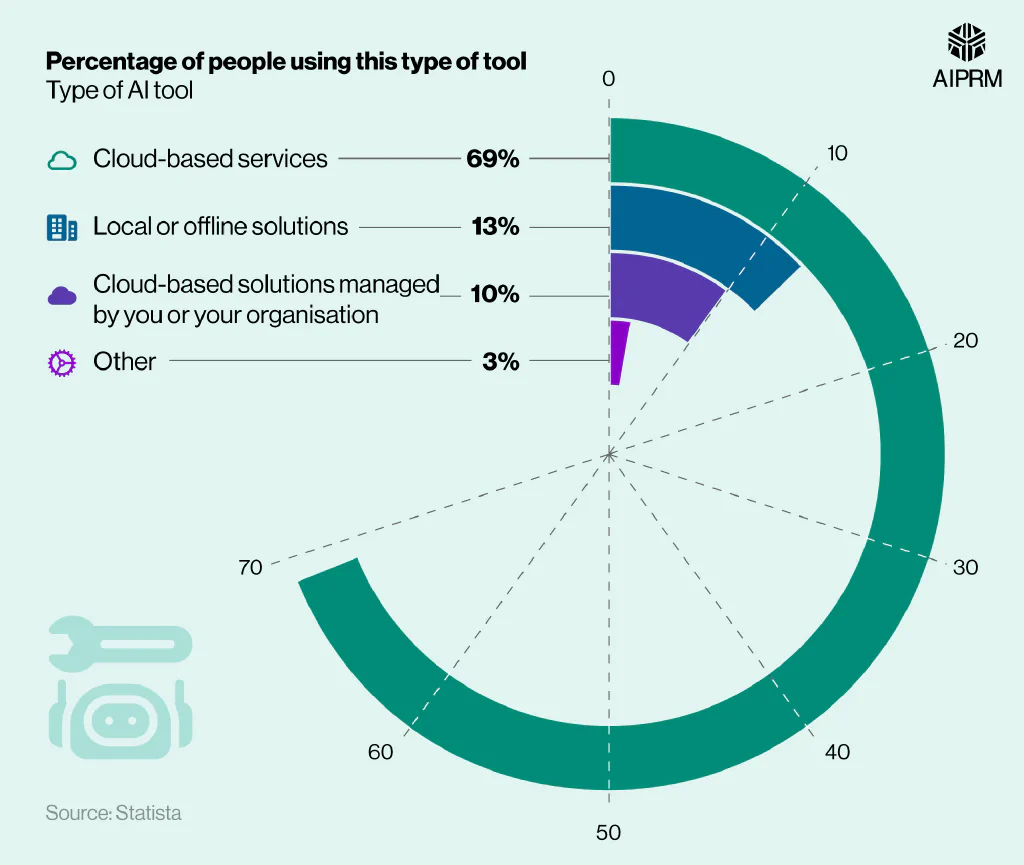
Over two-thirds (69%) of surveyed generative AI users claim they access the software via cloud-based service tools. This was five times more than the next most common response, with over a tenth (13%) claiming they access generative AI via local or offline solutions.
At the other end of the scale, only one in ten (10%) respondents used generative AI via their own personal or company-managed cloud-based tools.
Visit our expert blog for insight into a range of generative AI queries including using ChatGPT to create a social media strategy.
Generative AI in business #
A generative AI report from Google in 2023 surveyed more than 50 business leaders about their attitudes towards the technology.
Nearly two-thirds (64%) said they felt a high sense of urgency to adopt generative AI, with a further 62% feeling their organization lacks the critical skills required to execute their AI strategy.

The report also found that:
- Just 4% of organizations feel they have the required skills to achieve their AI goals.
- Seven in 10 (70%) were worried about generative AI giving out incorrect information.
- 70% felt marketing organizations stand to gain the most from generative AI.
A February 2024 report from the Financial Times found that more than nine in 10 (92%) companies in the Fortune 500 now use Open AI technology – the company behind ChatGPT. The same report found that over two million software developers are building on Open AI’s API, with the majority employed by Fortune 500 companies.
Which industries are adopting generative AI the most? #
Recent generative AI stats found that nearly two-fifths (37%) of professionals in the marketing and advertising industry used the software for work-related tasks in 2023. This was the highest total of any industry and at least 2% more than any other sector.
A breakdown of the percentage of companies using generative AI by industry in 2023 #
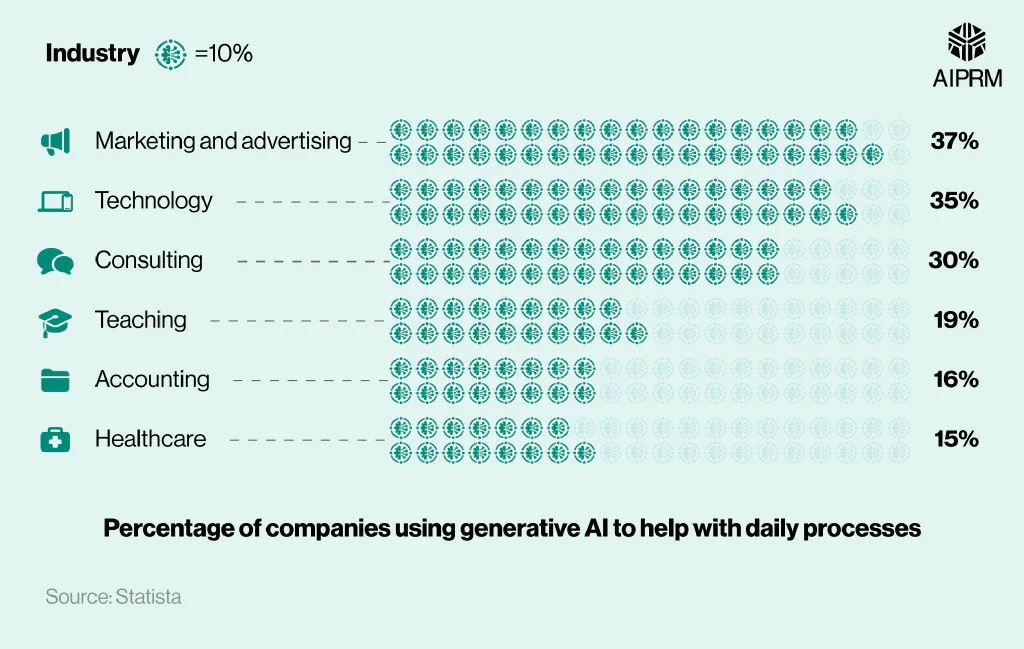
More than a third (35%) of workers in the technology industry stated they used generative AI for work tasks. This was 5% more than any other industry, making it the only other sector where more than one in three workers use generative AI.
Three in 10 (30%) consultants use generative AI in a professional capacity – 11% more than teachers (19%) and 14% more than accountants (16%).
Healthcare professionals were least likely to use AI for work, with their total of 15% less than half the number for both technology and marketing and advertising.
What are businesses’ main objectives when adopting AI? #
A report from McKinsey surveyed around 1,700 businesses on their uses and attitudes towards generative AI. The survey divided the organizations into standard businesses and ‘high performer AI’ businesses – companies that earned at least 20% of their earnings before tax from generative AI.
A third (33%) of regular businesses considered reducing costs in core business practices to be their primary aim for using generative AI – the joint most popular reason among this demographic. This number fell by 14% for high-performer companies, where just under a fifth (19%) gave this reason.
A breakdown of the primary objectives of businesses for integrating generative AI into their processes #
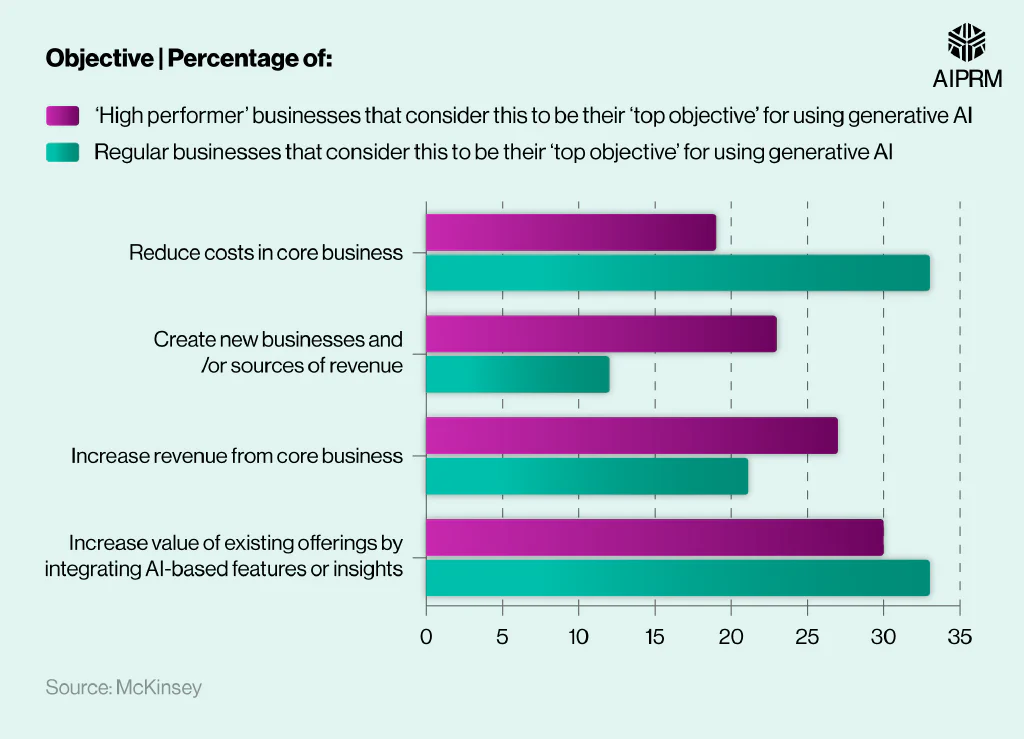
Creating new businesses or revenue sources was a more common objective among high performers, with nearly a quarter (23%) giving this response. This number almost halved for standard organizations, to 12%.
Over a quarter (27%) of high performers cited increasing revenue from their core business as their primary objective, with this number falling to just over a fifth (21%) for regular businesses.
Increasing the value of existing offerings was the most common objective amongst high-performing businesses, with three-tenths (30%) referencing this reason. This number rose to a third (33%) for regular companies – the joint most popular answer for this type of business.
Attitudes towards generative AI #
How will generative AI change the workforce? #
More than two-fifths (44%) of the businesses surveyed in McKinsey’s 2023 report expect generative AI to reduce their workforce in the following three years. A quarter (25%) expect their workforce to decrease by 3-10% with a tenth (10%) predicting cuts of between 11% and 20%. A further 8% expect their organization’s workforce to fall more than 20% by 2026.
A breakdown of how businesses feel generative AI will affect their workforce over the next three years (2023) #
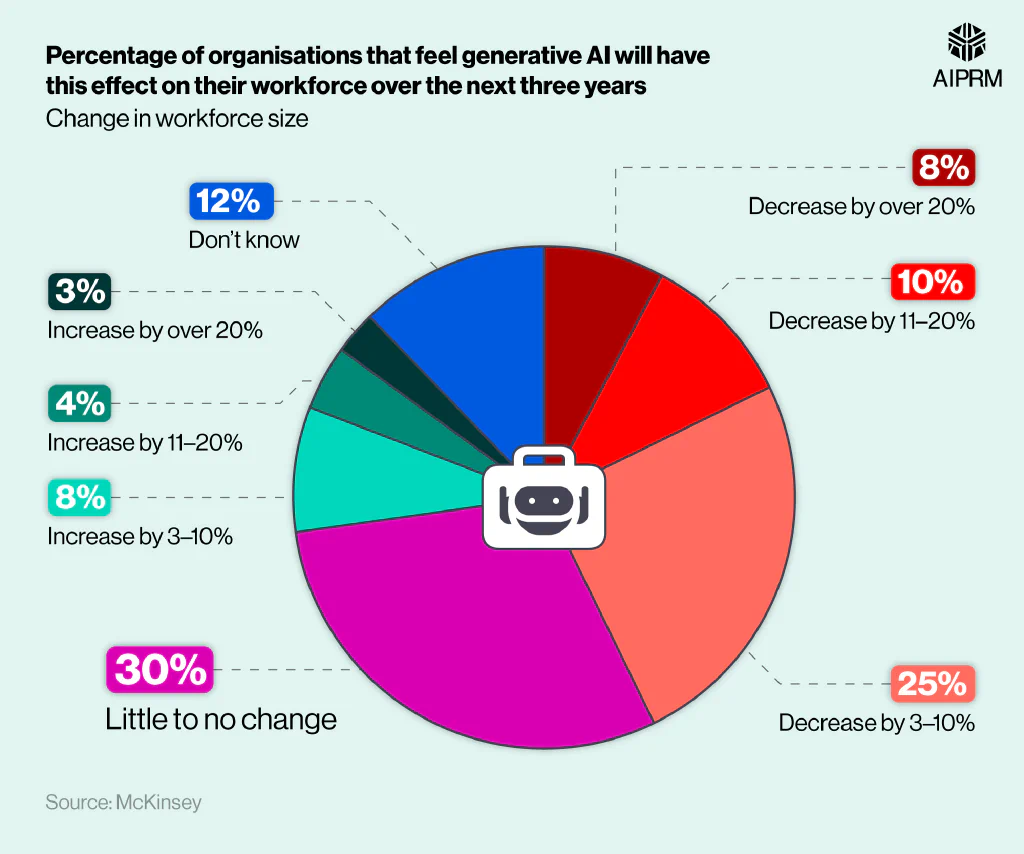
Around 15% of businesses believe generative AI would increase their workforce, with nearly a tenth (8%) believing these rises would be between 3% and 10%. Less than a twentieth (4%) of respondents believe generative AI would increase their staffing by 11-20%, with this number falling to 3% for rises above 20%.
Nearly a third (30%) think generative AI would have little to no change (2% or less either way) on their workforce, making this the most common view.
How many employees will need to be reskilled for generative AI? #
Generative AI statistics found that nearly two-fifths (38%) of businesses believe they’ll have to reskill over 20% of their employees due to generative AI. This was nearly double the number of any other response, with a fifth (20%) predicting they’ll only need to reskill 5% or less.
A breakdown of how many employees businesses feel will have to be reskilled in the wake of generative AI (2023) #
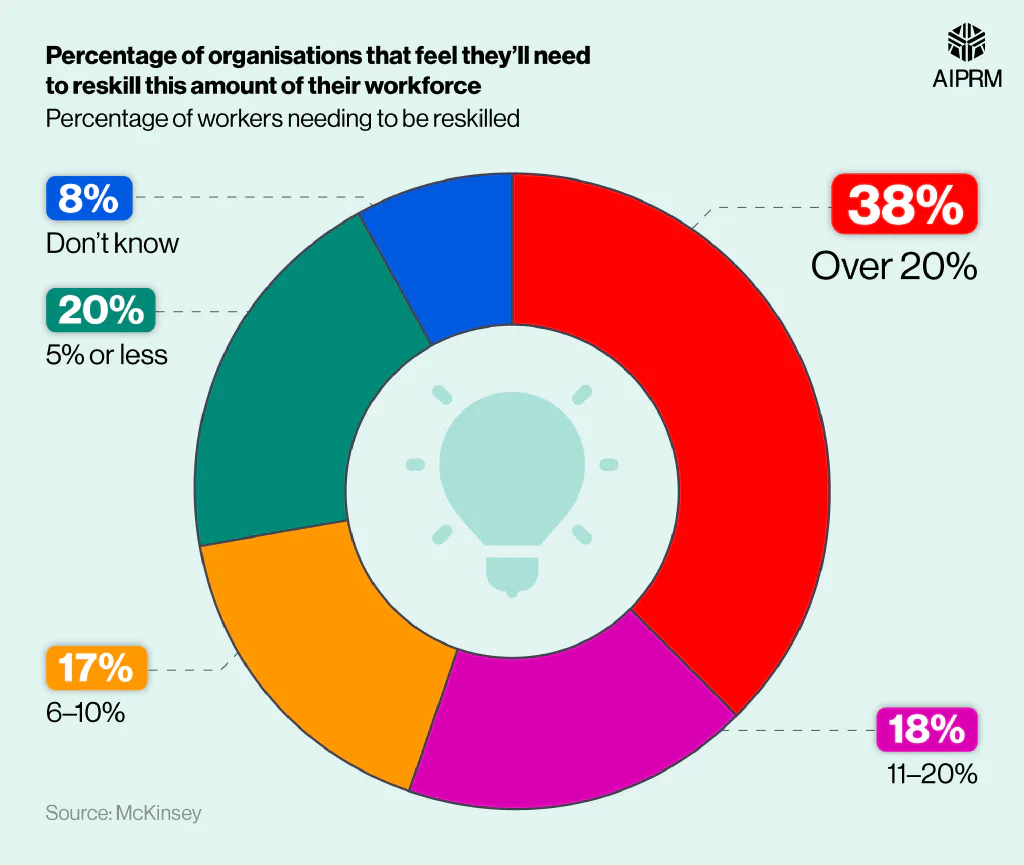
Just under a fifth (18%) believe they’d need to reskill between 11% and 20% of staff, with a further 17% expecting to retrain 6-10% of workers. Combined, this means nearly three-quarters (73%) believe they’ll have to retrain more than 5% of their employees.
Who uses generative AI? #
A report from Salesforce found that 70% of Gen Z have tried generative AI tools – the highest percentage of any generation.
The same report found that more than two-thirds (68%) of people unfamiliar with generative AI were baby boomers. Of these, two in five (40%) claimed they ‘didn’t know much’ about the software with a further 32% saying they ‘don’t find it useful.

Which generation has the most regular users of generative AI? #
Recent generative AI statistics found that just over a third (34.7%) of millennials use generative AI at least once a month, on average, in 2023. This is the highest number of any generation and represents a rise of more than 30% from 2022.
Gen Z had the next most regular users in 2023, at 33% – a rise of around 30% from 2022. The total number of monthly users fell to a quarter (25.6%) for Generation X and just over a tenth (12.9%) for Baby Boomers. However, this still represented annual rises of 22.8% and 11.6%, respectively.
A breakdown of the percentage of monthly generative AI users by year and generation #
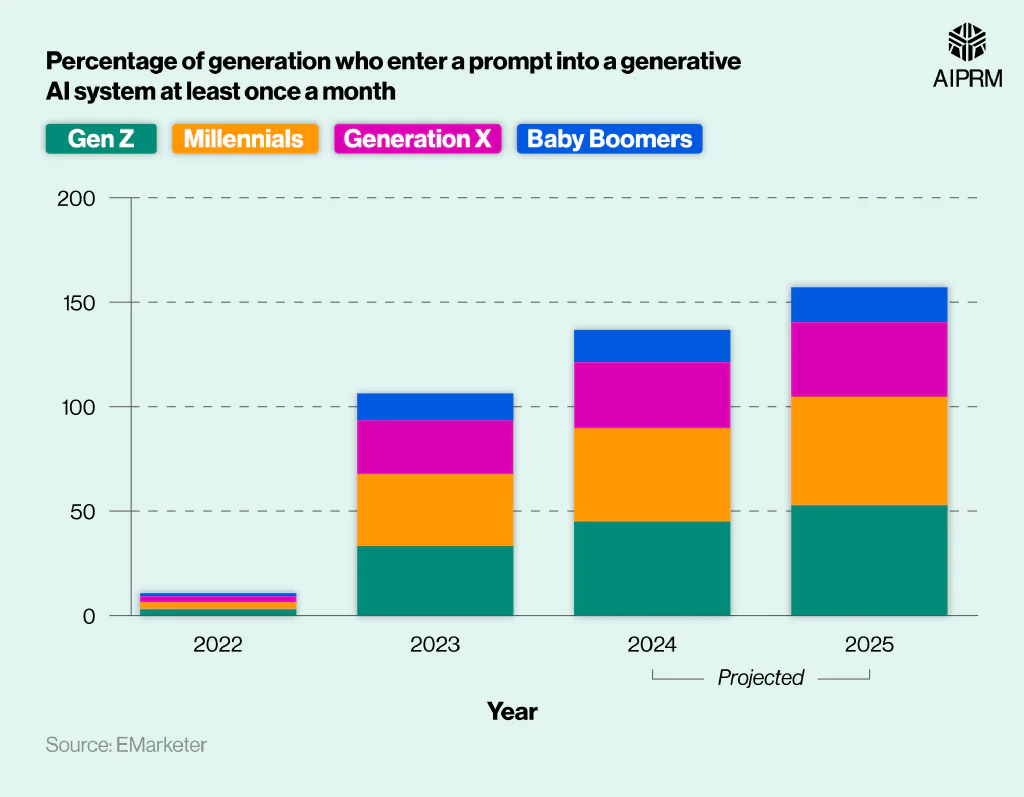
All generations are expected to see growth in regular generative AI usage in 2024 and 2025. Gen Z usage is expected to overtake millennials, reaching 45.1% in 2024 (+11.6%) before surpassing half (52.9%) by 2025. If correct, this would mean that the number of regular users increased by nearly 20% over two years.
Millennials could experience slightly slower growth, hitting 44.6% in 2024 (+9.9%) before reaching 52% (+7.4%) by 2025. Over a third (35.7%) of Generation X are expected to be regular generative AI users by 2025 – a two-year rise of 10.1%.
Baby boomers are predicted to see the slowest growth, rising to 15.5% in 2024 (+2.6%) before surpassing 16% in 2025 (+1.2%). Nevertheless, these rises would mean that regular use amongst baby boomers was more than 12 times higher in 2025 than in 2022.
Which gender uses generative AI the most? #
Analysis of generative AI stats shows a significant difference in usage among men and women in 2024. A global survey of 25,000 working adults found that almost three-fifths (59%) of men say they use generative AI, compared to just over half (51%) of women.
A global breakdown of the percentage of people using generative AI by age and gender (2024) #
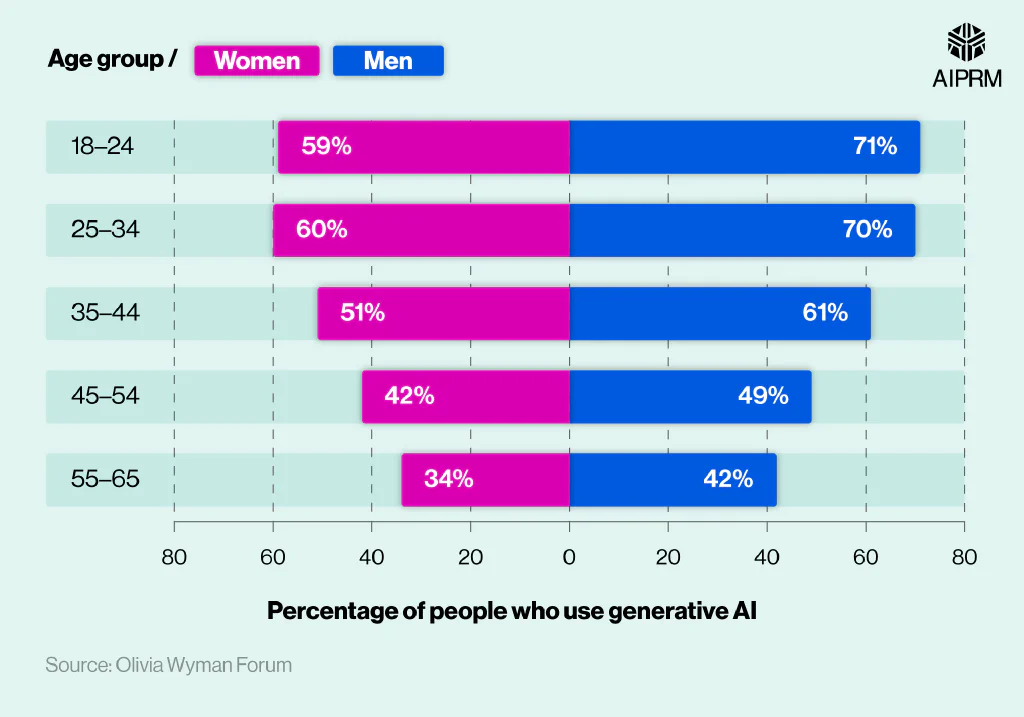
The gender gap in generative AI use was present in all age brackets, with the difference even greater among the youngest groups. Around seven in 10 (71%) men aged 18-24 use generative AI, compared to about three-fifths (59%) of women – the biggest difference of all age groups (12%).
This deficit fell to 10% for those aged 25-34 before dropping to 7% for those aged 45-54 – the smallest difference of all age groups. Just over a third (34%) of women workers in the oldest age group (55-65) said they used generative AI – 8% lower than men of the same age.
Which countries are most interested in generative AI? #
The Philippines leads the way when it comes to online interest in Generative AI, with the country averaging over 5,000 related monthly searches per 100,000 people in 2023 – nearly three-quarters (74%) more than any other nation.
Generative AI statistics show that Singapore had the next highest search volume, at 3,036. This was around two-fifths (37%) more than any other country, making Singapore the only other nation with more than 3,000 generative AI searches per 100,000 people.
A breakdown of the countries with the highest search volumes for generative AI #
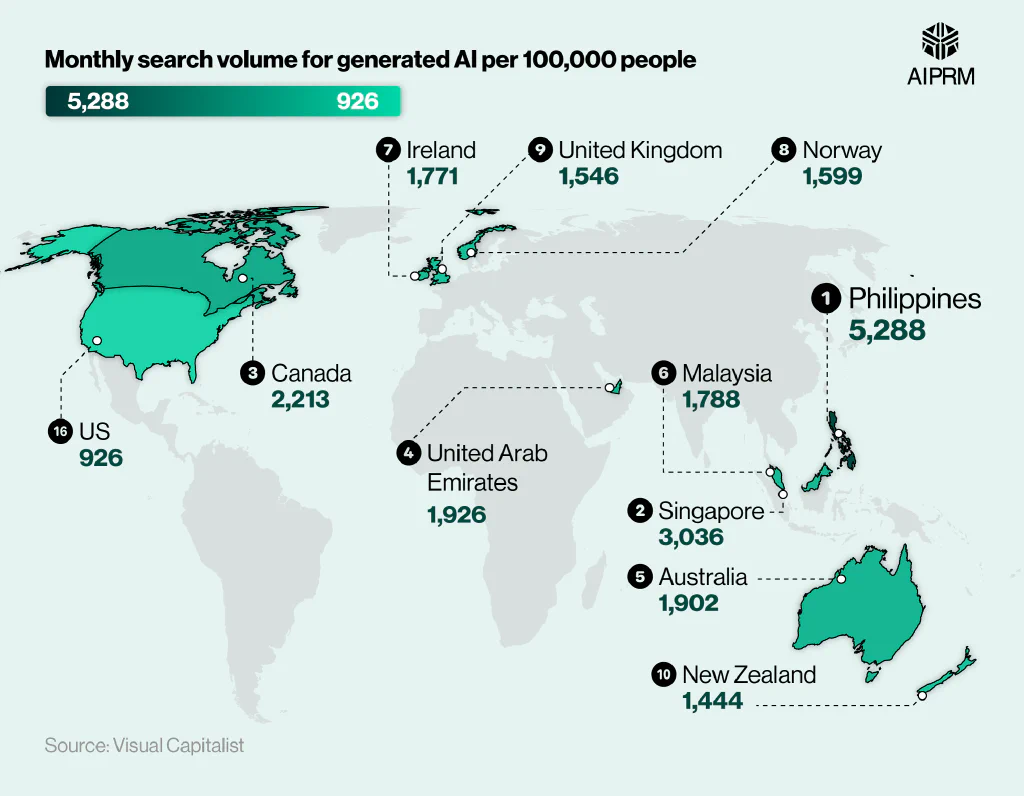
Canada’s total of 2,213 was the only other country with search volumes above 2,000 per month. This was 15% more than the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and 16% more than Australia – the countries with the fourth and fifth-highest search volumes, respectively.
Despite leading the way in the generative AI market, the US’ monthly search volume of 1,187 per 100,000 people was the 15th highest overall. This was around two-fifths (41%) less than Canada and more than three-quarters (-78%) less than the total for the Philippines.
Generative AI FAQs #
What is generative AI?
Generative AI is a form of artificial intelligence capable of generating text, images, videos, and other data in response to prompts from humans.
How does generative AI work?
Generative AI tools are powered by generative models – a type of machine learning that aims to identify patterns and structures in data.
Generative AI works by learning the patterns and structures of input training data, before generating its own output based on the patterns it has identified.
What is a prompt in generative AI?
AI prompts are instructions or queries inputted into a generative AI tool to illicit a response (output). Prompts can be in the form of text, questions, information, or code.
The purpose of a prompt is to let the generative AI tool know what response you’re looking for. By having specific and detailed prompts, you make it more likely that the tool will follow your requests accurately and generate the content you want. You can learn more about how to write effective prompts by visiting our guide.
Chatgpt, Google Bard, and Anthropic Claude are examples of which type of generative AI model?
Chatgpt, Google Bard, and Anthropic Claude are examples of large language models (LLMs). LLMs are a class of generative AI tool trained on massive text datasets to generate fluent, human-like responses. As such, these tools are typically used to answer queries or assist with text-based tasks.
What does the term model mean in generative AI?
A model is a generative AI that trains another AI tool on a dataset. Models work by identifying the underlying patterns in large datasets to formulate their own relevant responses.
The functionality of a generative AI tool will depend on the model it was trained with. For example, the ChatGPT premium version is more accurate and varied than the free version because it was trained on a more sophisticated model (ChatGPT 4 vs ChatGPT 3.5, respectively)
What is the primary advantage of using generative AI in content creation?
Generative AI vastly reduces the time required for repetitive and simple content tasks by producing the work much quicker than a human could manage. These tools also work well for research, offering quick and in-depth information that can be valuable before taking on a large writing task.
Lastly, generative AI can be great for providing inspiration before starting a piece of content. Many use the tool to produce sample content before writing something themselves, using the basic structure and information to inform their own work.
However, as a reactive tool, generative AI is no substitute for the uniqueness and creativity of a high-calibre piece of human-written content.
How can generative AI be used in cybersecurity?
Generative AI has the potential to bolster cybersecurity in numerous ways. The vast database of these models can be used for predictive analysis, reviewing past attack patterns and security breaches to predict potential future threats. From here, organizations can plan strategies to mitigate against these threats.
Generative AI can also analyse emails in mass to detect phishing and other common scams to help identify patterns associated with scamming attempts.
Finally, generative AI can be used in a testing capacity for cybersecurity. For example, cybersecurity professionals can use the software to create artificial malware samples that can be tested in a controlled environment. The findings from these tests can be used to hone an organization’s online security tactics and ensure they’re better prepared for real breaches in the future.
Generative AI glossary #
Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) #
CAGR is the average annual rate of growth over a set number of years. For example, if an industry grew by 20% over a four-year period, it would have a CAGR of 5% for those four years.
ChatGPT #
ChatGPT is a generative AI chatbot developed by OpenAI that uses large language models (LLMs) to perform tasks and answer queries. ChatGPT works by responding to user prompts to create humanlike images, text or videos.
Generative AI #
Generative artificial intelligence is a type of AI capable of generating text, images, videos, and code, usually by following human prompts.
Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS) #
Iaas is a cloud technology model that provides on-demand access to digital resources such as servers, storage, and networking.
Large Language Model (LLM) #
LLMs are machine learning models that analyse massive text datasets. They identify patterns and structures in text, to produce their own similar outputs.
Sources and methodology #
https://explodingtopics.com/blog/generative-ai-stats
https://www.statista.com/forecasts/1449838/generative-ai-market-size-worldwide
https://www.precedenceresearch.com/insights/generative-ai-market
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1413836/use-of-generative-ai-us/
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1413818/generative-ai-use-worldwide/
https://www.cbinsights.com/research/generative-ai-funding-top-startups-investors-2023/
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1413836/use-of-generative-ai-us/
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1413818/generative-ai-use-worldwide/
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1451117/generative-ai-tool-usage/
https://www.ft.com/content/81ac0e78-5b9b-43c2-b135-d11c47480119
https://www.statista.com/statistics/1361251/generative-ai-adoption-rate-at-work-by-industry-us/
https://www.salesforce.com/news/press-releases/2023/09/07/ai-usage-research/
https://www.emarketer.com/content/generative-ai-climb-across-all-age-groups-millennials-gen-z
https://www.weforum.org/agenda/2024/04/women-generative-ai-workplace/
https://www.visualcapitalist.com/cp/mapped-interest-in-generative-ai-by-country/